Human Resource Management Functions
February 27, 2024 2024-02-27 11:00Human Resource Management Functions
Human Resource Management Functions
Introduction
Human resource managers carry out the functions of human resource management to achieve the goals and objectives of the organization. Figure 5.1 illustrate the two set of functions, i.e. managerial functions and operative functions. The managerial functions are the fundamental functions human resource managers perform in the capacity of heads of their own departments. Really, all managers, regardless of their department, execute these functions. The operative functions are specialized jobs carried out exclusively by the HR managers, generally for all the departments. We shall, first, discuss the managerial functions.
Human Resource Management Functions
Human Resource Management functions may be categorized in to:
Managerial Functions, and
Operative Functions
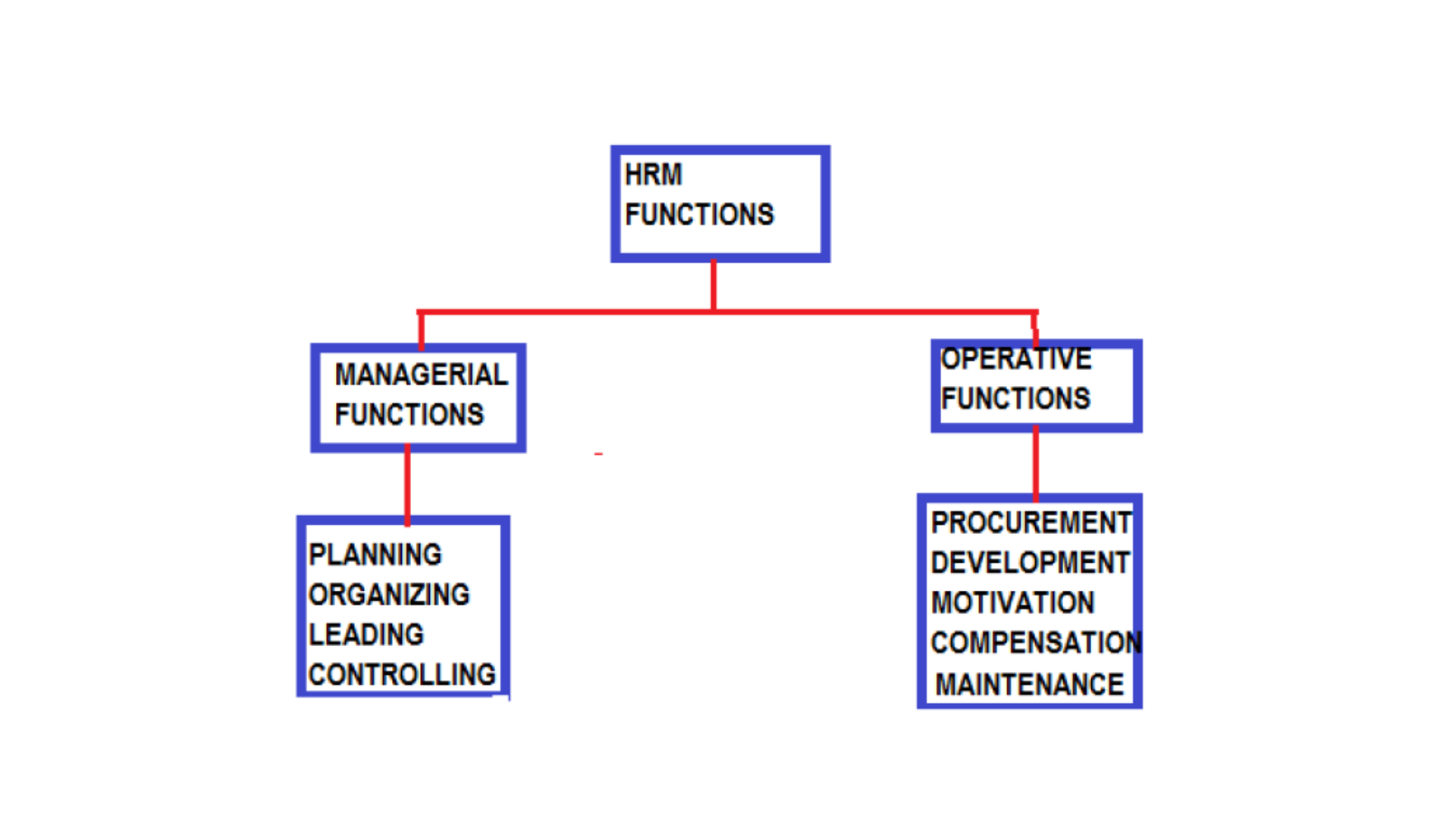
Managerial Functions
The Managerial Functions of Human Resource Management are as follows:
Human Resource Planning –
Human resource planning refers to the decision on the future course of action to accomplish desired goals. The number and type of employees required to achieve organizational goals is determined. Planning of human resources today avoids problems tomorrow. Research forms an important part of this function where information is gathered and analyzed to identify current and future needs of human resources and to forecast transforming values, attitudes, behavior of employees and their impact on organization.
Organizing
Organizing is primarily related with proper combining of personnel activities, allocation of different tasks among its members, delegation of authority, identification of relationships, and integration of activities towards a common objective. Designing of a proper structural framework is the primary task of organizing. Organizational relationships are created among the employees so that they can collectively contribute to the attainment of organizational goal.
Directing –
Directing involves overseeing and giving directions to the personnel. Proper direction and motivation makes it possible to activate employees at different level and make them contribute their maximum to the organization. In order to execute plans, direction is essential as without direction there is no destination. Many a time, the accomplishment of the organization goals relies on the direction of things. Direction embodies motivation and leadership. The HR manager must be an effective leader to create teams willing to add their contribution. In order to achieve, the personnel manager must, constantly, pay attention to the concerns and expectations of the employees at different levels.
Controlling
Controlling function of HRM comprises measures of the performance, comparing the results accomplished with the standards established. The managers identify and analyze the deviations, if any positive or negative attempt to know the reasons for deviations. It makes employee conscious of their performance through performance appraisal and audit programs. The controlling attempts to ensure that the activities are being carried out in accordance with stated plans.
Operative Functions
The operative functions of HRM are about the specific activities of procurement, developing, motivating, compensating and, maintaining employees. The operative functions are to be carried out in association with managerial functions.
The Operative Functions of Human Resource Management include:
Procurement of Human Resources
Procurement of Human Resources is the first operative function of Human Resource Management. This function is concerned with job analysis, planning of human resource, recruitment, selection, induction, orientation placement and internal mobility. Job analysis is the process of gathering information of the tasks and responsibilities of a particular job, depicting the nature of a job and stating the human requirements like qualifications, skills, and work experience to perform that job. Human resource planning ascertains and assures that the organization has enough qualified persons in adequate number, available at times when they are required, performing job. Recruitment of candidates is the function, which raises the pool of prospective candidates available to the organization so that the management can choose the suitable candidate from this common supply of people. Selection is the process of determining qualifications, experience, job skills and knowledge of an application with a view to appraising his suitability for the job in question. Placement matches the qualifications of the employees’, experience, skills and their interest in the job on offer. Induction and orientation are the techniques to rehabilitate a new employee in his new situation and made familiar to the practices, policies and people, and is acquainted with the principles, practices, values and objectives of the organization. Internal mobility of employees from one job to another takes place transfers and promotion.
Development
Development refers to the process to improve, mould, change and develops the knowledge, skills, creativities, aptitude, attitude, values and commitment of employees based on current and future requirements both at the person and organizational level. The development function includes training, development of executives, career planning and development, and human resource development. Training is concerned to the attainment of knowledge, skill development, and acquisition of competencies as a consequence of the teaching of the professional or practical skills and knowledge that relates to a specific job. Executive development is a systematic method of developing managing skills and capabilities through appropriate management development programs. Career planning and development consists of the planning of career and translating career plans into action through educating, training, job search and gaining of work experiences and succession planning. Human Resource development aims at developing the total organization by creating a climate of employee development for using his capability to achieve both individual and organizational goals.
Motivation
Motivation is a process which encourages people to bestow their best to the organization through the application of intrinsic and extrinsic rewards. The intrinsic rewards consist of achievement, recognition, and responsibility, extrinsic rewards consists of job design, work scheduling, incentives based on performance appraisal. Job design relates to organizing tasks and responsibilities for having a productive unit and integrating the needs of employers to fit the requirements of an enterprise. Work scheduling is carried out to motivate employees through job enrichment, reduced work weeks, flexi-time, sharing of work and work at home assignments. Combining forces that permit individuals to behave in definite ways is an integral tract of motivation. Employees need to have both the ability and the motivation to perform at high level. Managers usually make effort to motivate people through suitably administered rewards. Job evaluation is the technique to determine of relative worth of job in order to establish which job should be paid more than others within the organization and establish internal equality between various jobs. Performance evaluation is the method of evaluating the behavior of employees at the place of work and usually includes the quantitative as well as qualitative dimensions of of job performance. It is an objective and systematic method of evaluating work-related behavior and potential of employees. It determines and communicates to an employee how he is performing and establishing a plan of improvement.
Compensation and Incentives
Compensation administration is the process of deciding how much an employee is likely to be paid. The important goals of compensation management are to design a low-cost pay plan that will attract, motivate and retain competent employees. In addition to a basic wage structure, most organizations usually offer incentives based on actual performance. Unlike incentives, all employees receive benefits and services as law requires involving social security, insurance, compensation for workmen’s and welfare amenities etc. Organizations have been offering a basket of benefits and services such as employees’ stock options, gifts given to employees on their birthday, marriage anniversary, paid holidays and membership of a club.
Maintenance
Maintenance aims at guarding and preserving the physical and mental health of employees through health and safety, employee welfare and social security measures. Organizations at all levels are expected to enforce safety and health standards. Managers must ensure a work environment that protects employees from physical dangers, unhealthy conditions and unsafe actions of coworkers. Proper safety and health programs may help in preserving and improving the physical and mental well-being of employees.
Employee welfare involves providing the services, amenities and affording the facilities offered to employees in and outside the organization for their all round well being. The employee welfare package includes housing, transportation, education and recreation facilities.
The employees generally receive social security in addition to fringe benefits. These measures include Workmen’s compensation to worker who are involved in accidents, maternity benefit to women employees, sickness benefits and medical benefits, disability benefit, dependent benefits, and retirement benefits.
Integration Function
The integration function aims to integrate the goals of an organization with employees’ strong desired through several employee-directed programs, like grievance redress, disciplinary measures, empowering people to take decisions independently, encouraging a culture of employee participation in decision making and offering constructive assistance to trade unions etc.
Constructive grievance handling depends on the ability of a manager to recognize, diagnose and set right the causes of potential employee dissatisfaction before it convents into a formal grievance. Discipline is the force that promotes an individual or a group to follow the rules, regulations and procedures deemed necessary for the attainment of an objective.
Self-managed teams have come up as the most important formal groups in organizations today. They enhance employee involvement and increase the potential to create positive synergy. Enhancing worker mutual influence, they create good fellowship among members of a team and encourage individuals to diver energy from individual goals to those of the group. Teams have inseparable strengths which ultimately lead to organizational success at various levels.
Collective bargaining is the process of reaching an agreement between management and union. The contract includes mutual arrangements about terms and conditions of employment, like wages, hours of work, promotions, and discipline; lay- off, fringe benefits, paid holidays, rest pauses and the management of grievances. In collective bargaining management and workers both tend to put proposals and counter proposals generally takes time, as both. The resulting agreement must be ratified by unions, workers and management.
Managements also encourage employee participation and empowerment. Participation profess sharing the power of decision-making with the lower ladders of an organization in an appropriate manner to enable them to see the big picture clearly and also the manner in which their actions would influence the growth of the company. Since the workers are not treated with respect, they begin to see the job and the organization as their own, and commit themselves to organizational objectives whole-heartedly.
The trade unions aim to counter exploitation and harassment and pay a powerful role in improving the lot of workers using aggressive bargaining tactics. Harmonious industrial between labor and management are essential to achieve industrial growth and higher productivity.
Emerging Functions
Effective management of human resources relies on make HRM practices finer to changing conditions. Hence there is the need to focus on other important factors that can motivate employees to give their best in a dynamic and ever-changing environment. Such emerging issues are maintenance of personnel records, human resource audit, HR research, human- resource accounting system, stress and counseling and international human resource management.
Personnel records such as papers, files, cards, cassettes and films are maintained to record of what is actually happening in an organization and to formulate appropriate HR policies and programs from time to time.
Human resource audit is an examination and evaluation of policies, procedures and practices to evaluate the effectiveness of HRM. Human resource research evaluates the effectiveness of human resource policies and practices so that more appropriate policies and practices are developed. Human resource accounting measures cost and value of human resources for the enterprise.
Human resource information systems is an integrated system directed to improve the efficiency in collection of HR data by making HR records more useful to the management and by serving as a source of information. In an organization burn out is the outcome stress, increased absenteeism and increased turnover. Through counseling and employee development programs companies are trying to promote the physical and mental wellbeing of employees.
International human resource management poses many challenges before managers including coordinating different operations on a worldwide basis. International HRM places greater importance on a variety of responsibility and functions such as relocating, providing orientation and training to assist employees adjust to an unfamiliar and distinct environment from their own country.
HR Policies
Once the objectives of the organization are established, HR policies are to be formulated. Policies are common assertions that guide thinking and action for taking decisions.
Definition of HR Policy
Human resources policies guide action, offer the general standard or yardsticks for decision-making, work as a guide for managers on various issues such as recruitment, selection, promotion and compensation. HR policies are usually derived from the HR objectives of the organization and summarize the past experience in terms of valuable guidelines to help manager and speed up the decision-making process. They assist managers and subordinates for the disposal of routine matters and permit managers to delegate some of the repetitive problems to subordinates. Thus, HR policies are significant means of transferring a part of decision-making to lower hierarchies of organization.
Types of HR Policies
Human resources policies may be categorized on the basis of their source, scope and form.
Originated policies:
Top management establishes originated policies deliberately to guide executive thinking at different levels
Appealed policies are formulated to satisfy the needs of certain peculiar situation uncovered by earlier policies on the request on subordinates who find it difficult to resolve certain issues.
Imposed policies are the outcome of pressures of government, trade associations and unions.
General policies reflect the basic philosophies and priorities of the top management in the formulation of overall plan for the organization’s growth map.
Specific policies include issues such as hiring, rewarding and bargaining and should be in consonance with the basic framework of general policies
Written or implied policies are drawn from behavior of members including dress code, gentle tone at the time of talking to customers, remaining calm at work etc. and spell out managerial thinking to spare little space for loose interpretation
Objectives of HR Policies
HR policies as useful instructions, serve several purposes and objectives for the organization. Some important objectives are:
Delegation: HR policies assist operating- managers act with confidence without consulting superiors every time.
Uniformity: They provide uniformity for making choices at various levels of the organization when independently face similar situation and make the actions more consistent.
Control measure: The HR policies allow members to strive for achievement of the objectives of the organization as they specify the relationship divided between the organization, management and its employees.
Standards of Efficiency: HR policies are able to serve as standards in the execution of work and enable the management to visualize if the various groups convert policies into action.
Coordination: HR policies assist in achieving coordination. The organizational members guided by the same policies can easily predict the action and decision of other and ensure a steady course of action and avoid unwarranted deviations from standards.
Confidence: Personnel policies create confidence among people while encountering routine and repetitive matters and reduce possibilities of misinterpretation and friction and enable speedy decision making.
Formulation of HR Policies
Formulation and implementation of HR policies involves the following steps:
Need Identification
At the beginning significant areas of human resource management consists recruitment and selection, training, compensation and collective bargaining, need to have a clearly spelt out policy formulation. In addition policy guidelines may come in at a later stage depending on the recurrence of difficult issues at different levels.
Collection of data:
The next step in the policy formulation is to collect facts needed for formulating a HR policy. Different sources such as records of the company, practices in the past, survey of industry practices, experience of personnel handling different issues, philosophy of top management, organizational culture, aspirations of employees and changes in economic, social and legislative environment etc could be utilized for these purposes.
Specifying alternatives:
Policy alternatives are likely to emerge clearly after the relevant data from various sources has been collected. These alternatives should be evaluated in respect of their contribution to organizational objectives. People at various levels should also be involved, especially those such policies influence. Top management should approve the policies only after everything is set and the stated policy clearly represents organizational priorities.
Communicating the policy:
The formulated policy should be communicated to all in the organization to get approval at various levels, Discussions with people may take place at various levels, policy manual and in house journal may also be of assistance to re approach to employees quickly. Special coaching programs can also communicate people about the manner of implementation.
Evaluation of the Policy:
In order to be effective, HR policies need be reviewed, evaluated and controlled constantly against prior established standards to assist determine changes in existing policies. All the policies require annual review, while some need be reviewed at specific times. Employees, consultants or experts may take part in the review of policies.
HR Procedures and Programs
Policies are brief statements and do not describe specifically the way policy is to be implemented. Procedures implement policies. A procedure is a well thought out course of action prescribing the specific manner in which a work is to be done. They are ‘action guidelines’ derived from policies. Where policies define a broad field, procedures demonstrate a chronological, step-by-step sequence of activities within that area
Conclusion:
Broadly, human resource management functions may be categorized into: managerial functions, operative functions, integrative function and emerging function. Managerial functions include planning, organizing, leading and controlling; operative function consists of procurement, development, motivation, compensation and incentives, maintenance.
The integration function aims to integrate the goals of an organization with employees’ aspirations through various employee-oriented programs, like grievance redress, disciplinary measures, empowering people to take decisions independently, encouraging a culture of participation of employee in decision making and constructive assistance to trade unions etc.
Emerging issues are maintenance of personnel records, human resource audit, HR research, human- resource accounting system, stress and counselling and international human resource management.
Human resources policies guide action, offer yardsticks for decision-making, serve as a plan for managers on various issues such as recruitment, selection, promotion and compensation.
Major types of HR policies include originated, appealed, imposed, general, specific, written or implied policies.
Main stages in the formulation of HR policies need identification, collection of data: specifying alternatives, communicating the policy and evaluation of the Policy:






