HRP Process
January 20, 2024 2024-03-01 13:33HRP Process
HRP Process
HRP Process
HRP effectively involves forecasting personnel needs, assessing personnel supply and matching demand– supply factors through personnel related programmes. The HR planning process is influenced by overall organizational objectives and environment of business.
The HRP Process
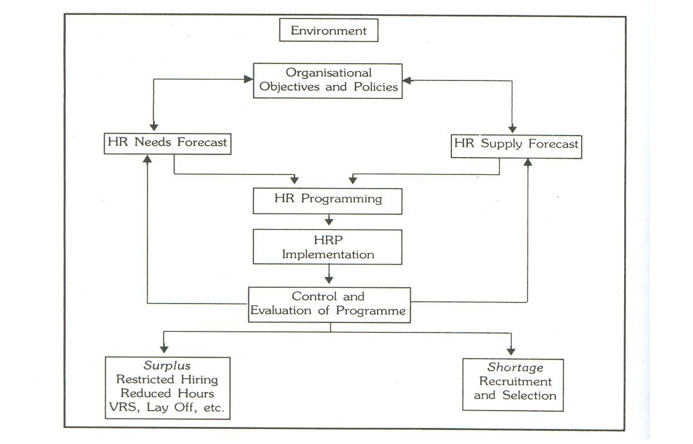
Environmental Scanning:
It refers to the systematic monitoring of the external forces influencing the organization. The following forces are essential for pertinent HRP.
- Economic factors, including general and regional
- Technological changes
- Demographic changes including age, composition and literacy,
- Political and legislative issues, including laws and administrative rulings
- Social concerns, including child care, educational facilities and
By scanning the environment for changes that will affect an organization, managers can anticipate their impact and make adjustments early.
Organizational Objectives and Policies: HR plan is usually derived from the organizational objectives. Specific requirements in terms of number and characteristics of employees should be derived from organizational objectives
Once the organizational objectives are specified, communicated and understood by all concerned, the HR department must specify its objective with regard to HR utilization in the organization.
HR Demand Forecast:
Demand forecasting is the process of estimating the future quantity and quality of people required to meet the future needs of the organization. Annual budget and long-term corporate plan when translated into activity into activity form the basis for HR forecast.
For eg: in the case of a manufacturing company, the sales budget will form the basis for production plan giving the number and type of products to be produced in each period. This will form the basis upon which the organization will decide the number of hours to be worked by each skilled category of workers. Once the number hours required is available organization can determine the quality and quantity of personnel required for the task.
Demand forecasting is influenced by both internal factors and external factors: external factors include- competition, economic climate, laws and regulatory bodies, changes in technology and social factors whereas internal factors are budget constraints, production level, new products and services, organizational structure and employee separations.
Demand forecasting is essential because it helps the organization to
1. Quantify the jobs, necessary for producing a given number of goods,
2. To determine the nature of staff mix required in the future,
3. To assess appropriate levels in different parts of organization so as to avoid unnecessary costs to the organization,
4. To prevent shortages of personnel where and when, they are needed by the organization.
5. To monitor compliances with legal requirements with regard to reservation of jobs.
Techniques like managerial judgment, ratio- trend analysis, regression analysis, work study techniques, Delphi techniques are some of the major methods used by the organization for demand forecasting.
HR Supply Forecast:
Supply forecast determines whether the HR department will be able to procure the required number of workers. Supply forecast measures the number of people likely to be available from within and outside an organization, after making allowance for absenteeism, internal movements and promotions, wastage and changes in hours, and other conditions of work.
Supply forecast is required because it is needed as it
- Helps to quantify the number of people and positions expected to be available in future to help the organization realize its plans and meet its objectives
- Helps to clarify the staff mixes that will arise in future
- It assesses existing staffing in different parts of the organization.
- It will enable the organization to prevent shortage of people where and when they are most needed.
- It also helps to monitor future compliance with legal requirements of job reservations.
Supply analysis covers the existing human resources, internal sources of supply and external sources of supply.
HR Programming:
Once an organization’s personnel demand and supply are forecasted the demand and supply need to be balanced in order that the vacancies can be filled by the right employees at the right time.
HR Plan Implementation:
HR implementation requires converting an HR plan into action. A series of action are initiated as apart of HR plan implementation. Programmes such as recruitment, selection and placement, training and development, retraining and redeployment, retention plan, succession plan etc when clubbed together form the implementation part of the HR plan.
Control and Evaluation:
Control and evaluation represent the final phase of the HRP process. All HR plan include budgets, targets and standards. The achievement of the organization will be evaluated and monitored against the plan. During this final phase organization will be evaluating on the number of people employed against the established (both those who are in the post and those who are in pipe line) and on the number recruited against the recruitment targets. Evaluation is also done with respect to employment cost against the budget and wastage accrued so that corrective action can be taken in future.
Requisites for Successful HRP
- HRP must be recognized as an integral part of corporate planning
- Support of top management is essential
- There should be some centralization with respect to HRP responsibilities in order to have co-ordination between different levels of
- Organization records must be complete, up to date and readily
- Techniques used for HR planning should be those best suited to the data available and degree of accuracy
- Data collection, analysis, techniques of planning and the plan themselves need to be constantly revised and improved in the light of
Barriers to HRP
Human Resource Planners face significant barriers while formulating an HRP. The major barriers are elaborated below:
- HR practitioners are perceived as experts in handling personnel matters, but are not experts in managing The personnel plan conceived and formulated by the HR practitioners when enmeshed with organizational plan, might make the overall strategic plan of the organization ineffective.
- HR information often is incompatible with other information used in strategy Strategic planning efforts have long been oriented towards financial forecasting, often to the exclusion of other types of information. Financial forecasting takes precedence over HRP.
- Conflict may exist between short term and long term HR For example, there can be a conflict between the pressure to get the work done on time and long term needs, such as preparing people for assuming greater responsibilities. Many managers are of the belief that HR needs can be met immediately because skills are available on the market as long as wages and salaries are competitive. Therefore, long times plans are not required, short planning are only needed.
- There is conflict between quantitative and qualitative approaches to Some people view HRP as a number game designed to track the flow of people across the department. Others take a qualitative approach and focus on individual employee concerns such as promotion and career development. Best result can be achieved if there is a balance between the quantitative and qualitative approaches.
- Non-involvement of operating managers renders HRP HRP is not strictly an HR department function. Successful planning needs a co-ordinated effort on the part of operating managers and HR personnel.
Summary
Today, human resource planning is viewed as the way management comes to grasp the ill-defined and tough-to-solve human resource problems facing an organization. Human resource planning is the process of determining the human resources required by the organization to achieve its goals. Human resource planning also looks at broader issues relating to the ways in which people are employed and developed, in order to improve organizational effectiveness. HRP is a decision making process that combines activities such as identifying and acquiring the right number of people with the proper skills, motivating them to achieve high performance and creating interactive links between business objectives are resource planning activities. HRP sets out requirements in both quantitative and qualitative terms. Accurate manpower plan is a dream. A common error of many managers is to focus on the organization’s short term replacement needs. Any human resource plan, if it is to be effective, must be derived from the long term plans and strategies of the organization. The various approaches to human resource planning under which a number of major issues and trends in today’s work plan that will affect organization and employees are
(1)Examine external and internal issues,
(2) Determining future organizations capabilities,
(3) Determining future organizational needs, and
(4) Implementing human resources programmes to address anticipated problems. Although change is occurring very rapidly in the work world it is important for both organizations and employees to monitor issues and events continuously and consider their potential effects.
Read More – https://hranalyticspro.com/a-comprehensive-guide-to-15-roles-and-responsibilities-of-hr/






