What is Human Resource Management?
January 19, 2024 2024-01-20 9:35What is Human Resource Management?
What is Human Resource Management?
What is Human Resource Management
HRM is the study of activities regarding people working in an organization. It is a managerial function that tries to match an organization’s needs to the skills and abilities of its employees.
Definitions of HRM
Human resources management (HRM) is a management function concerned with hiring, motivating and maintaining people in an organization. It focuses on people in organizations. Human resource management is designing management systems to ensure that human talent is used effectively and efficiently to accomplish organizational goals.
HRM is the personnel function which is concerned with procurement, development, compensation, integration and maintenance of the personnel of an organization for the purpose of contributing towards the accomplishments of the organization’s objectives. Therefore, personnel management is the planning, organizing, directing, and controlling of the performance of those operative functions (Edward B. Philippo).
According to the Invancevich and Glueck, “HRM is concerned with the most effective use of people to achieve organizational and individual goals. It is the way of managing people at work, so that they give their best to the organization”.
According to Dessler (2008) the policies and practices involved in carrying out the “people” or human resource aspects of a management position, including recruiting, screening, training, rewarding, and appraising comprises of HRM.
Generally HRM refers to the management of people in organizations. It comprises of the activities, policies, and practices involved in obtaining, developing, utilizing, evaluating, maintaining, and retaining the appropriate number and skill mix of employees to accomplish the organization’s objectives. The goal of HRM is to maximize employees’ contributions in order to achieve optimal productivity and effectiveness, while simultaneously attaining individual objectives (such as having a challenging job and obtaining recognition), and societal objectives (such as legal compliance and demonstrating social responsibility).
In short Human Resource Management (HRM) can be defined as the art of procuring, developing and maintaining competent workforce to achieve the goals of an organization in an effective and efficient manner.
Nature of HRM
HRM is a management function that helps manager’s to recruit, select, train and develop members for an organization. HRM is concerned with people’s dimension in organizations.
The following constitute the core of HRM
- HRM Involves the Application of Management Functions and The functions and principles are applied to acquiring, developing, maintaining and providing remuneration to employees in organization.
- Decision Relating to Employees must be Integrated. Decisions on different aspects of employees must be consistent with other human resource (HR)
- Decisions Made Influence the Effectiveness of an Organization. Effectiveness of an organization will result in betterment of services to customers in the form of high quality products supplied at reasonable
- HRM Functions are not Confined to Business Establishments Only but applicable to non- business organizations such as education, health care, recreation and
HRM refers to a set of programmes, functions and activities designed and carried out in order to maximize both employee as well as organizational effectiveness.
Scope of HRM
The scope of HRM is indeed vast. All major activities in the working life of a worker – from the time of his or her entry into an organization untilhe or she leaves the organizations comes under the purview of HRM. The major HRM activities include HR planning, job analysis, job design, employee hiring, employee and executive remuneration, employee motivation, employee maintenance, industrial relations and prospects of HRM.
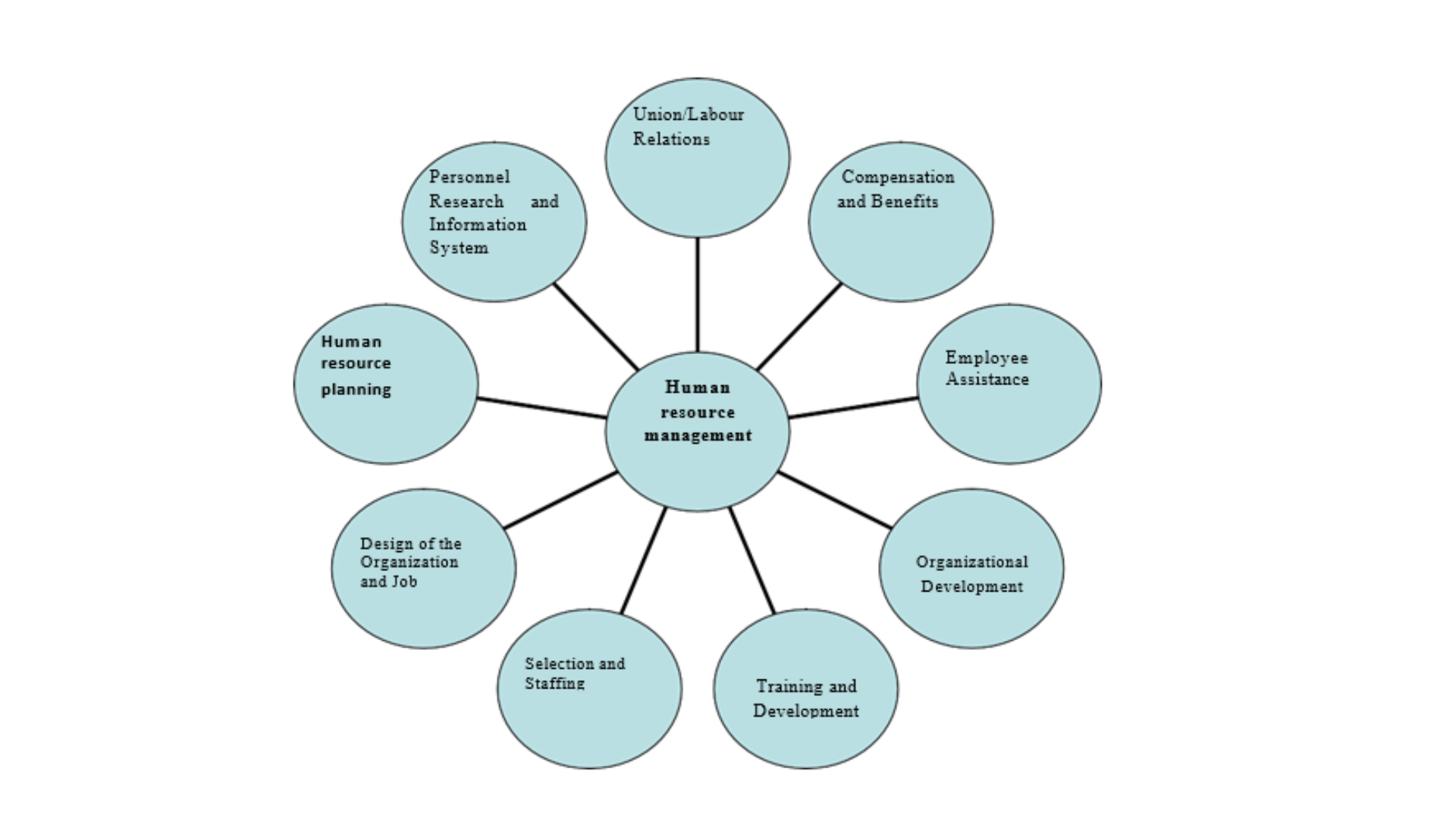
The scope of Human Resources Management extends to:
- All the decisions, strategies, factors, principles, operations, practices, functions, activities and methods related to the management of people as employees in any type of
-
- Human Resource Planning: The objective of HR Planning is to ensure that the organization has the right types of persons at the right time at the right It prepares human resources inventory with a view to assess present and future needs, availability and possible shortages inhuman resource. Thereupon, HR Planning forecast demand and supplies and identify sources of selection. HR Planning develops strategies both long-term and short-term, to meet the man-power requirement.
- Design of Organization and Job: This is the task of laying down organization structure, authority, relationship and This will also mean definition of work contents for each position in the organization. This is done by“job description”. Another important step is “Job specification”. Job specification identifies the attributes of persons who will be most suitable for each job which is defined by job description.All the dimensions related to people in their employment relationships, and all the dynamics that flow fromThe scope of HRM is really vast. All major activities n the working life of a worker – from the time of his or her entry into an organization until he or she leaves it comes under the purview of HRM. American Society for Training and Development (ASTD) conducted fairly an exhaustive study in this field and identified nine broad areas of activities of HRM.These are given below:
- Human Resource Planning
- Design of the Organization and Job
- Selection and Staffing
- Training and Development
- Organizational Development
- Compensation and Benefits
- Employee Assistance
- Union/Labour Relations
- Personnel Research and Information System
- Selection and Staffing: This is the process of recruitment and selection of This involves matching people and their expectations with which the job specifications and career path available within the organization.
- Training and Development: This involves an organized attempt to find out training needs of the individuals to meet the knowledge and skill which is needed not only to perform current job but also to fulfil the future needs of the
- Organizational Development: This is an important aspect whereby “Synergetic effect” is generated in an organization e. healthy interpersonal and inter-group relationship within the organization.
- Compensation and Benefits: This is the area of wages and salaries administration where wages and compensations are fixed scientifically to meet fairness and equity In addition labour welfare measures are involved which include benefits and services.
- Employee Assistance: Each employee is unique in character, personality, expectation and By and large each one of them faces problems everyday. Some are personal some are official. In their case he or she remains worried. Such worries must be removed to make him or her more productive and happy.
- Union-Labour Relations: Healthy Industrial and Labour relations are veryimportant for enhancing peace and productivity in an This is one of the areas of HRM.
- Personnel Research and Information System: Knowledge on behavioral science and industrial psychology throws better insight into the workers expectations, aspirations and Advancement of technology of product and production methods have created working environment which are much different from the past. Globalization of economy has increased competition many fold. Science of ergonomics gives better ideas of doing a work more conveniently by an employee. Thus, continuous research in HR areas is an unavoidable requirement. It must also take special care for improving exchange of information through effective communication systems on a continuous basis especially on moral and motivation.
HRM is a broad concept; personnel management (PM) and Human resource development (HRD) are a part of HRM.






